Due diligence and supply chains
The Guidelines acknowledge and encourage the positive contributions of the enterprises to the economic, environmental and social, but also acknowledge that their activities can have a negative impact in areas such as corporate governance, labour rights, human rights, environment, corruption and consumer interests.
In particular, the enterprise are required to adopt a responsible business conduct and to:
- avoid causing or contributing to adverse impacts on matters covered by the Guidelines, through their own activities, and address such impacts when they occur;
- seek to prevent or mitigate an adverse impact where they have not contributed to that impact, when the impact is nevertheless directly linked to their operations, products or services by a business relationship. This is not intended to shift responsibility from the entity causing an adverse impact to the enterprise with which it has a business relationship;
- in addition to addressing adverse impacts in relation to matters covered by the Guidelines, encourage, where practicable, business partners, including suppliers and sub-contractors, to apply principles of responsible business conduct compatible with the Guidelines.
In order to do all this effectively, the OECD Guidelines recommend companies to implement a due diligence, i.e. a “process through which enterprises can identify, prevent, mitigate and account for how they address their actual and potential adverse impacts as an integral part of business decision-making and risk management systems”.
To support companies effectively in the implementation of this process, the OECD has developed a series of sectoral guides. lastly, a general due diligence guide.
The due diligence process
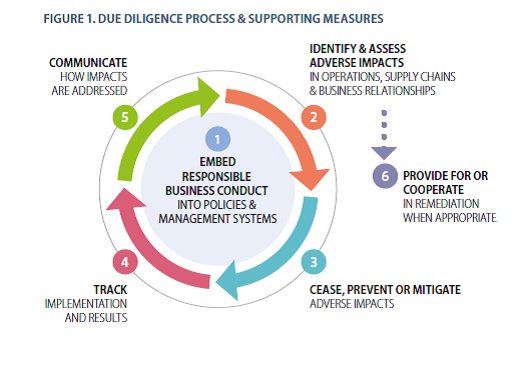
- Embed responsible business conduct into policies and management systems.
- Identify and assess actual and potential adverse impacts associated with the enterprise’s operations, products or service.
- Cease, prevent and mitigate adverse impacts.
- Track implementation and results.
- Communicate how impacts are addressed.
- Provide for or cooperate in remediation when appropriate.
The guides
- OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Business Conduct [General guidance]
- OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Meaningful Stakeholder Engagement in the Extractive Sector
- Sourcing gold from artisanal and small-scale gold mining
- OECD due diligence guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas
- Practical actions for companies to identify and address the worst forms of child labour in mineral supply chains
- OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains in the Garment and Footwear Sector
- OECD-FAO Guidance for Responsible Agricultural Supply Chains
- Responsible Business Conduct for Institutional Investors. Key considerations for due diligence under the OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises
- Preventing Corruption and Promoting Responsible Business Conduct when Organising Sporting Events


